TUMESCENT, WET & ULTRASONIC LIPO EXPLAINED
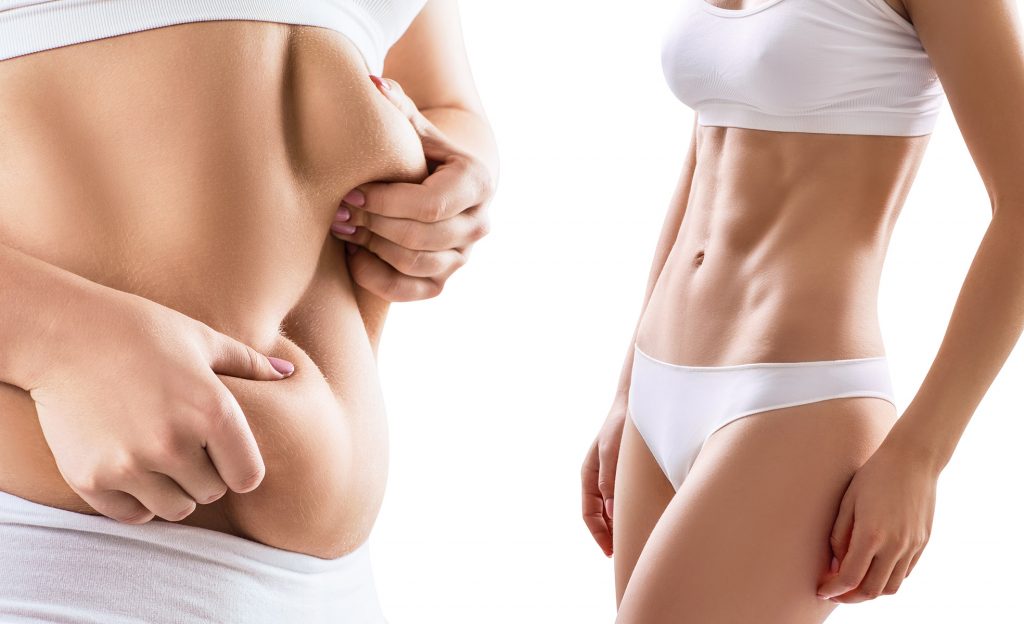

Liposuction is the most common plastic surgery procedure performed in the United States. In a liposuction procedure, a small hollow needle called a cannula is used to remove fat through suction as it creates tunnels through the fat tissue beneath the skin. As your body heals, the tunnels collapse and the result is a better-contoured body. This is also why liposuction is often referred to as body contouring.
Since much of the results from liposuction occur as the tunnels from the cannula heal, the full effect of a liposuction procedure is often not seen for up to a year. Thousands of men and women across the country have chosen to have liposuction in the past year, and some of the most common areas to have the procedure performed on are:
- Inner/Outer Thighs
- Arms
- Gynecomastia (Enlarged Male Breasts)
- Waist
- Hips/Saddlebags
- Chin/Jaw Line
- Neck
- Calf
- Buttocks
- Back
- Ankle
- Abdomen
Liposuction is performed in a wide variety of ways. Tumescent, wet, super wet, ultrasonic (UAL), and power assisted (PAL) are all techniques for performing liposuction. All of these techniques are used to provide the patient with the results they are looking for.
Tumescent liposuction is performed by first injecting very diluted solution of lidocaine, epinephrine, and saline into the fat. Lidocaine acts as a local anesthetic, while the epinephrine causes the capillaries in the fat to constrict; the solution causes the fat tissue to swell and become firmer. Since the capillaries are constricted from the epinephrine, the lidocaine takes a longer amount of time to be absorbed by the body.
This means that the patient does not need to go under general anesthetic for the procedure, there is usually no need for an IV as a result of fluid loss, and the amount of blood lost is minimal as opposed to other forms of liposuction.
The wet liposuction technique requires the use of general anesthesia and injecting the area with a dilute solution of local anesthesia in order to reduce the amount of bleeding. Of the tissue removed, blood comprised about 15% to 20% of all the tissue removed from the body. The wet technique is hardly ever used anymore because of the need for blood transfusions after the procedure.
The super wet technique also requires general anesthesia and the injection of dilute local anesthesia. With this technique, blood still comprises about 8% of the total tissue removed.
The difference between the tumescent liposuction technique and the wet and super wet liposuction techniques is the amount of solution injected into the subcutaneous fat (fat beneath the skin). The super wet technique only uses about half of the solution the tumescent technique and the wet technique uses very little lidocaine solution at all, which is why general anesthesia is needed.
UAL, or Ultrasonic Assisted Liposuction, involves the process of using a metal probe or paddle to deliver ultrasonic energy to the fat, liquefying it. This makes the fat easier to remove and leaves other tissues like nerves and blood vessels intact.
PAL, or Power Assisted Liposuction, uses a power supply to create a spinning or in-and-out movement in the cannula. This technique is used to perform the procedure in a smaller amount of time.
Liposuction is not an alternative to weight loss and should only be used as after all other options have been exhausted. The ideal candidate for liposuction:
- Is normal or slightly overweight
- Has elastic skin
- Has areas of excess fat
- Is physically healthy
- Is psychologically healthy
- Has realistic expectations
Since liposuction is not for everyone, schedule an initial consultation with a plastic surgeon in your area to find out if the surgery is right for you. Your plastic surgeon will discuss with you about the results you want, and can realistically achieve, and which liposuction technique is the best approach to achieving those results.