By Michele Boyer
TUBA and Trans-Axillary Breast Augmentation are both endoscopic procedures, and both offer the advantage of avoiding incisions and scars on the breast. Choosing between these two breast augmentation procedures means deciding the outcome you want, where you will have to go for the surgery, and knowing the pros and cons of each procedure.
| TUBA Technique | Trans-Axillary Technique | |
| Incision – Pros | 1″ – 1.5″ inside naval rim. No scars on breasts.. Only one incision is needed for both implants. Elasticity of skin and natural folds camouflage incision and help it remain small. Only about 1/2 teaspoon of blood lost.. Less chance of infection. Best choice for larger implants – no incision to stretch.. Incision is nowhere near the breast.. Scars are essentially undetectable. | 1″ – 1.5″ scar in each armpit. No scars on breasts.. Some claim it best for full sub-muscular placement.. Incision made in natural folds of skin is less visible than crease or areola incisions. Scars almost invisible after 3 years. Scars that are minimally visible are not usually noticed, or even associated with breast surgery. Working closer to breast than from TUBA site. |
| Incision – Cons | Requires tunneling from the naval to the breast, leaving temporary “tracks”. While the tracks usually disappear after healing, occasionally they are permanent. Requires working farther from the breast than axillary, areola and crease sites. If this method fails and implant placement is unsatisfactory, the usual alternative sites are areola or crease. | Scars can be visible when arms are raised. If placed blindly (without endoscope) can result in lopsided placement. Requires working farther from the breast than areola and crease sites. More surgeons are trained in this technique than TUBA. |
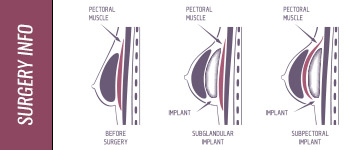
| Options – Pros | May have sub-glandular, partial or full sub-muscular placement. | May have sub-glandular, partial or full sub-muscular placement. Can be used for silicone implants. |
| Options – Cons | Breast lift not reasonable as it would require an incision on the breast, resulting in an unnecessary naval incision. Repair of complications such as “bottoming-out”, symmastia, and capsulectomy are too difficult to perform via an axillary incision. Cannot be used for silicone implants. There are fewer surgeons trained in this technique than others. | Breast lift not reasonable as it would require an incision on the breast, resulting in an unnecessary naval incision.. Repair of complications such as “bottoming-out”, symmastia, and capsulectomy are too difficult to perform via an axillary incision. |
| Surgery & Recovery – Pros | Less operating room time.. Endoscopic surgery is less invasive and less traumatic. The milk ducts are not disturbed. Surgery takes less than an hour. Less invasive. Less recovery time than with on-breast sites; about 36-48 hours, half of other methods; about same as Trans-axillary. Less breast trauma. No incision on the breast means no tension on the incision, thus less pain. Less chance of infection. | More surgeons are trained in this technique than in TUBA.. Endoscopic surgery is less invasive and less traumatic.. Less recovery time than with on-breast sites; about 36-48 hours, half of other methods; about same as TUBA. |
| Surgery & Recovery – Cons | Finding qualified, experienced surgeon. | Requires 2 incisions and more operating room time. Somewhat greater chance of infection than TUBA. |