MALE BREAST TISSUE REMOVAL
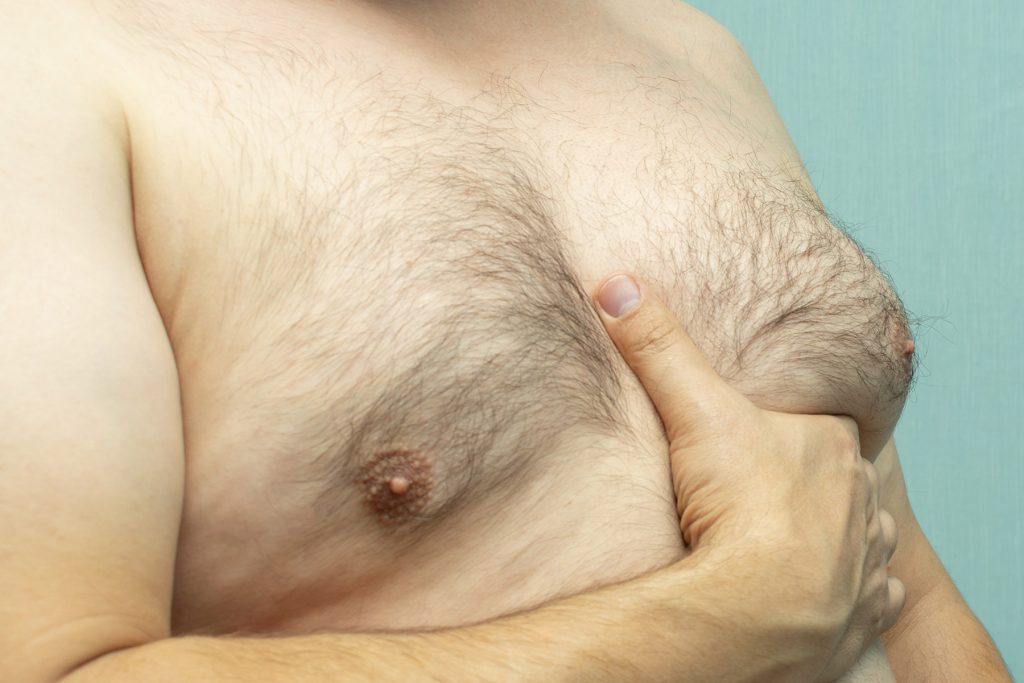
Gynecomastia, a condition in which men develop female-like breasts, is remarkably common, but rarely discussed. While gynecomastia is estimated to affect as many as 40 to 60 percent of adult men, most people are unfamiliar with the condition, its causes, and the treatments available.
Men suffering from gynecomastia should consult with a doctor to determine the root cause of the condition first. Only after determining the cause of the condition can treatment options be evaluated.
Gynecomastic breasts in men are composed either of excess fat, excess glandular tissue, or some combination of the two. The causes of the condition, however, are much more varied. Gynecomastia can be the result of obesity, hormonal changes, aging, a side effect of medication (such as Risperdal), or of medical conditions such as liver disease and certain genetic disorders.
Before considering treatment options for gynecomastia, it is important to establish the cause of the condition. In some cases, the underlying cause must be treated for the patient’s health, and the symptom will disappear once the condition is treated.
In many cases, too, gynecomastia is a transient condition that will either go away on its own, as is frequently the case when boys develop the condition during puberty; or that can be best treated by lifestyle changes such as weight loss or altering regular medication under a doctor’s supervision.
While some root causes of gynecomastia are dangerous to the health, it is not a physically dangerous condition in itself. However, the psychological effects can be damaging. Men suffering from gynecomastia may experience self-consciousness, embarrassment and shame, and a variety of psychological issues related to sexual identity. While gynecomastia is not in any way a reflection of a man’s sexuality, many men suffer from sexual insecurities due to the feminine appearance of their breasts.
In cases in which the gynecomastia is permanent and cannot be managed by weight loss or other lifestyle changes, male breast reduction surgery is an option that should be evaluated with a reputable plastic surgeon.
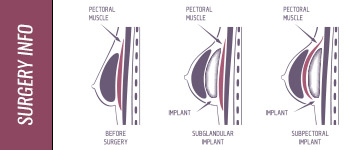
In such cases, the procedure will vary depending on the extent of the problem and whether the gynecomastic breasts consist of fat, glandular tissue, or both.
The process used to remove excess fat is a liposuction procedure in which fat is removed through a small tube inserted in a small incision on the edge of the areola, the area of darker skin surrounding the nipple.
The process used to remove excess glandular tissue involves excision, or cutting out the tissue with a scalpel. In most cases, the incision will be made inconspicuously, on the edge of the areola or under the arm, and the surgeon will work through the incision to remove the tissue. Depending on the individual patient, the surgeon may also remove excess fat and skin during the procedure as necessary.
For major reductions, the surgery is generally more extensive, and may involve multiple procedures, including both the liposuction and excision described above, as well as additional procedures to remove excess skin so it lays flat over the patient’s chest post-surgery.
Most breast reduction surgeries will be performed under general anesthesia, or, in some cases, a combination of local anesthesia and sedation; and the recovery procedure takes several weeks before full activities can be resumed. The results of the breast reduction, however, are permanent and should not require further treatment after the healing process is complete.