A-H | I-Q | R-Z
R
Radiesse® – An injectable filler containing tiny calcium-based microspheres in a water-based gel. The gel is gradually absorbed by the body, leaving the microspheres in place as temporary volume plumping up the skin. Gradually the skin grows more collagen fibers around the microspheres, extending the effectiveness of Radiesse to about two years. Treatment must then be repeated.
Reduction Mammaplasty – See Breast Reduction.
Restylane® – An injectable filler that plumps up the skin, smoothing out wrinkles and fine lines. It is based on hyaluronic acid, a substance found naturally in the body adding fullness to the skin. Often used for lip augmentation, as it plumps up those small lines, and for crows feet, forehead wrinkles, and hollow areas around the eyes.
Retin-A – A derivative of Vitamin A used to treat acne, whiteheads and blackheads. It also helps with wrinkles. Also called Tretinoin.
Retinol – A substance derived from Vitamin A which is found in skin care products.
Rhinoplasty – Nose surgery. It is done to reshape or resize the nose and involves resculpting of the bone and cartilage in the nose. It can include correction of a deviated septum.
Rhytid – Medical term for a wrinkle.
Rhytidectomy – Wrinkle removal. See Facelift.
Rosacea – A skin condition with symptoms such as redness and puffiness on the face. Causes are unknown and there is no cure. It can be controlled, especially if it is caught early. Ocular rosacea is often found along with the skin condition.
S
Saline – Adjective meaning salty. Also used to refer to the saline solution used in medical procedures which has the same salinity as human body fluids. Therefore it does not affect the body’s chemical balance.
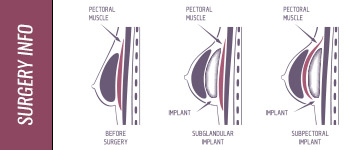
Saline Implants – Breast implants which are filled with saline solution. They have silicone shells and are usually inserted empty, then filled to the desired fullness. If the shell were to rupture and the saline solution were to leak, it would be harmlessly absorbed.
Scar – A build-up of fibrous connective tissue. It is the body’s way of healing a cut or incision. Scarring is largely an individual thing, with some people scarring easily and quickly and others developing large unsightly scars known as Keloid Scars or Hypertrophic Scars. Typically, it takes about a year for a scar to fully fade and shrink.
Scar Revision – Surgery to reduce the size of a scar.
Sclerotherapy – Reduction or elimination of spider veins or varicose veins. The veins are injected with a solution that closes them off from the circulatory system, so that they fade away after a few weeks. Lasers can also be used.
Sculptra – An injectable filler based on lactic acid. It is synthetic, but biocompatible. Used to treat skin folds and hollow areas on the face. Results last about two years and then treatment is repeated.
Sebaceous Glands – Oil glands in the second skin layer, the dermis.
Septoplasty – Surgery to modify or reconstruct the nasal septum.
Septum – A thin wall that divides two cavities, as between the two nostrils. See Deviated Septum. The columella is the fleshy area at the front of the septum where a small incision is made during open rhinoplasty.
Silicon – The second-most-common of Earth’s elements, after oxygen. It is in such omnipresent objects as sand, rock and crystals. Forms of silicon are used in everyday household products such as dish detergent, hairspray and hand lotions.
Silicone – A modified form of silicon, used in breast implants, and the implants used for chin augmentation and cheek augmentation.
Silicone Gel Implants – Breast implants filled with silicone gel. For 14 years, they were restricted to reconstructive use by the FDA while further safety studies were done. In November, 2006, the FDA approved them again, in slightly modified forms. They have a strong silicone shell, as do saline implants, and are filled with a type of silicone gel which sticks to itself. That means that in the unlikely event that the shell ruptured, the gel would not leak.
Skin Graft – Living skin taken from the body or from a donor, and transplanted to another part of the body. Used in burn treatments and hair transplants.
Skin Resurfacing – Cosmetic enhancement of aging skin by removal of the epidermis. This stimulates the dermis to produce new, tighter skin cells. It can be done with lasers, chemical peels, dermabrasion, or microdermabrasion.
SOOF Lift – SOOF stands for Sub-Orbicularis Oculi Fat pad. A facial cosmetic surgery which repositions the fat pads below the eyes. It can be done along with blepharoplasty of the upper eyelids. It takes a different approach to the lower eyelids than blepharoplasty, which removes the fat rather than repositioning it for a fuller cheek area.
Spider Veins – Enlarged veins that become visible as we age. They are smaller versions of Varicose Veins. They can be caused by hormonal changes, genetic factors, obesity, pregnancy, increasing age, and sun exposure. They most often form on the legs or face and look blue or purple and like spider web lines.
Stratum Corneum – The top sub-layer of the skin’s top layer, the epidermis, which has five sub-layers.
Subcutaneous – Below the skin. Also the term for the fat-storing third layer of skin, beneath the dermis.
Suction Lipectomy – Another name for Liposuction.
Sun Protection Factor – Abbreviated as SPF. A measure of the effectiveness of sunscreens. An SPF of at least 15 would usually be recommended after any cosmetic skin procedures. SPF can be as low as 4, as in some lip balms, or as high as 60.
Super-Wet Liposuction – An early form of liposuction, devised to improve on Wet Liposuction. The small amount of fluid injected in Wet Liposuction allowed too much bleeding. Super-Wet Liposuction injects a larger amount of saline solution before fat removal. The next improvement was Tumescent Liposuction, where about twice as much fluid is injected as in Super-Wet.
Suture – Medical name for a stitch, done to close an incision.
T
Temporal Lift – Another name for a Brow Lift.
Thermage® – The name of a skin care company in California. Also their name for a cosmetic procedure for tightening the skin. Radio waves are used to heat the dermis while keeping the epidermis cool. This heats the collagen in the dermis, making it thicken and contract. This is termed Denaturation and it gives the skin a smoother look. At the same time, the heating stimulates the collagen to reproduce itself. This reverses the reduction of collagen that aging causes, and gives a more long-term tightening of skin cells. Other names for this process are ThermaCool® and ThermaLift™.
Thigh Lift – Cosmetic surgery to remove excess skin and fat from the thighs.
Titan™ – A skin tightening procedure using infrared light to stimulate collagen contraction. It heats the dermis while cooling the epidermis, like Thermage, and can be used on any area of the body. There is no pain and no downtime.
Trans-axillary – Location of a breast implant incision in the armpit.
Tretinoin – See Retin-A.
TUBA – Stands for Trans Umbilical Breast Augmentation. It refers to the location of the incision, at the belly button. This method is not used much any more, because of its greater distance from the implant site.
Tumescent Liposuction – Liposuction done after a large amount of saline solution is injected to the treatment area. The saline solution contains lidocaineas a local anesthetic and epinephrine to close off local blood vessels and prevent bleeding. The injected fluid helps with suctioning out the fat and creates more room in the treated area for the surgeon’s cannula movements.
Tummy Tuck – The popular name for Abdominoplasty.
Twilight Anesthesia – Another name for intravenous (IV) sedation. General anesthesia produces complete unconsciousness and is used for major surgery. Twilight anesthesia is most often used for outpatient procedures or dental work in anxious patients. It blocks pain and reduces awareness of the procedure being done, but allows the patient to respond to any requests made. The IV line remains in the patient’s vein until surgical work is finished, administering a steady drip of the medication mixture.
U
Ultrasound – Sound energy outside the range that humans can hear (but not beyond what some animals can hear, such as cats, dogs, bats, mice, and dolphins). It is an energy used in medical imaging, such as sonograms of a baby in the womb. Ultrasound is safe and widely used. In Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction, it is used to break up the fatty tissue to make it easier to suction out. cf Computed Tomography Scan.
Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction – Abbreviated as UAL. A liposuction technique which uses ultrasound energy to break down the fat cell membranes, making the fat more liquid and easier to remove.
Ultraviolet – A vibration of energy that produces colors invisible to humans. They are beyond the violet end of the color spectrum. Some lasers have an ultraviolet vibration, such as the excimer laser used in LASIK vision correction.
Umbilicoplasty – See Belly Button Surgery.
Unilateral Gynecomastia – Male breast enlargement on one side only.
Upper Arm Lift – Cosmetic surgery to remove excess fat and skin on the upper arms.
V
Varicose Veins – Enlarged veins, usually in the legs. The name comes from the Latin word varix which means twisted. Veins carry the blood returning to the heart. To prevent backflow, they contain valves which open and close as the blood is pumped through. As we age, the valves can weaken and allow blood to pool, which stretches the vein and distorts its smooth line.
Treatment is either to close them off to disconnect them from the circulatory system, or to surgically remove them. They can be closed off by injections, lasers, or catheter procedures. See also Spider Veins.
W
Wet Liposuction – An early way of performing liposuction, where a small amount of saline solution was first injected. It is not done any more, as improved methods now inject much more of that solution. It contains epinephrine, which has the effect of locally shrinking blood vessels, which dramatically reduces bleeding.
Wrinkle – A fold or furrow in the skin which has several causes such as sun damage, skin dryness, and reduced amounts of collagen in the dermis. There’s a collagen and elastin matrix in the dermis which supports the skin, giving it a smooth, youthful surface. As we age, we produce less collagen and the matrix weakens. Most skin rejuvenation methods are aimed at stimulating the collagen to produce more cells.
Z
Z-Plasty – Scar revision. It can be done to help hide a scar, as it uses a Z-shaped incision. This makes a three-part scar which is not as obvious as a straight line. It’s also done to correct a contracted scar, to change the line of tension in a scar and to reduce a scar’s size (in the case of Keloid Scars and Hypertrophic Scars. Also called Zigzagplasty.