A-H | I-Q | R-Z
I
Implant – A surgically placed device to enhance the appearance of part of the body. Examples are breast implants, and the implants used in Chin Augmentation and Cheek Augmentation.
Incision – A deliberate, surgical cut in the skin and body tissue beneath it. Incised skin always has a residual scar, although cosmetic surgeons will always try to place incisions such that the scar will be hidden, or barely visible.
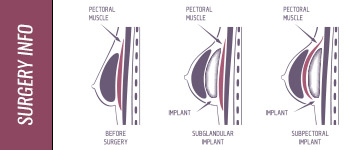
Inframammary – Referring to placement of a breast implant incision beneath the breast in the crease.
Injectable Filler – A biocompatible substance injected into the facial areas to give more fullness to the skin and smooth out lines and wrinkles. Effectiveness lasts for a few months up to about two years, and treatments are then repeated. Examples are Restylane®, Radiesse® and Perlane®.
J
Jowl – A pocket of loose skin and fat hanging below the jawline.
Juvederm – An injectable filler based on hyaluronic acid.
K
Keloid Scar – Excess scarring tissue that spreads beyond the original wound or incision. It becomes raised and red, and irregularly shaped. It results from too much collagen production in the dermis. See also Hypertrophic Scar.
Keratin – A protein found in hair, nails and the top layer of skin (epidermis). It adds hardness to those structures.
Kojic Acid – A skin-bleaching agent.
L
Lasers – Directional lights each man-made for a specific purpose and classified according to the medium used to make them: solid, gas, liquid or semi-conductor. A laser is set at a specific vibration, which is to say, a specific color. It can be a visible color or one that we can’t see – infrared or ultraviolet. Because the lightwaves travel in a parallel formation, lasers can be very finely focused, which makes them useful in surgery.
Some lasers are far too hot and powerful for use on human tissue. Those used in dentistry, vision correction, and surgeries are on the cooler end of the spectrum and usually have some type of cooling system as well, to protect tissue that’s not being treated. Laser heat is directed to the treatment area and in cosmetic surgery this precise heat can be used for a variety of treatments, e.g. to stimulate tissue rejuvenation, disable hair follicles, or cauterize veins.
Laser Hair Removal – Use of a soft-tissue laser to remove hair permanently by destroying the hair follicles.
Laser Skin Resurfacing – Use of a soft-tissue laser to stimulate the skin’s dermis to produce new, tighter skin cells. It can be done by ablating the skin’s epithelium, or by directly targeting the dermis (non-ablative skin resurfacing).
Lidocaine – An anesthetic used in the liposuction saline solution.
Lip Augmentation – A procedure to correct sagging lips, to plump up fine lines or wrinkles around the lips, or to increase the fullness of the lips. An implantmay be used, or injectable fillers.
Lipoplasty – See Liposuction.
Liposculpture – Liposuction done with a focus on revealing the body’s muscle contours rather than just removing a certain amount of fat. Also called High Definition Liposuction.
Liposuction – A procedure to remove excess fat from selected body areas. A cannula is used to suction out the fat. It may use ultrasound to first emulsify the fat. In tumescent liposuction, a large amount of saline solution is first injected to expand the treatment area, giving more room for the surgeon to work, and making it easier to remove the fat. Also known as Lipoplasty.
M
Male Pattern Baldness – Hereditary thinning of the hair in men, usually from the top of the head, leaving hair around the sides of the head.
Mammogram – X-ray of breast tissue. When breast implants are present, a mammogram is done a little differently, easing the implant out of the way. Also, more views are taken in the effort not to miss any cancerous growth.
Mammoplasty – Any surgical reshaping of the breast, whether done for reconstruction or cosmetic purposes.
Mandible – The lower jaw.
Mastectomy – Surgical removal of all or part of the breast.
Mastopexy – See Breast Lift.
Maxilla – The upper jawbone, part of the skull. It extends up around the nose and partly under the eyes.
Maxillofacial – Relating to the face and jaw area.
Melanin – Pigment. In humans it is in the skin, hair, eyes, and some internal organs. It is the primary cause of a person’s skin color.
Melanocyte – A cell which produces melanin.
Melanoma – Skin cancer, which can spread quickly if it is not treated early.
Melasma – Darkened skin discoloration, often occurring in pregnant women. It occurs in patches, usually on the face, and is thought to be caused by hormones such as are taken for hormone replacement therapy or oral contraception. They stimulate melanocytes to produce more pigment, which is darkened further by sun exposure.
Microdermabrasion – A skin resurfacing technique which uses small crystals to remove the epidermis. This stimulates the dermis below to produce new skin cells which look younger. It is a more gentle version of Dermabrasion.
Micropigmentation – A type of tattooing used to apply permanent makeup. Iron oxide is injected into the second skin layer, the dermis.
N
ND:YAG laser – Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet laser (referring to the materials from which it is generated). It is a solid-state, pulsed, infrared laser, used for hair removal and treatment of minor vascular defects such as spider veins.
Nasal – Pertaining to the nose
Nasolabial Folds – The deep wrinkles that develop as we age between the nose and corners of the mouth.
Neck Lift – Cosmetic surgery to remove excess skin in the neck to treat horizontal bands or “turkey neck”. Often done with liposuction to remove the excess fat.
Nose Job – Popular term for rhinoplasty.
Non-Ablative Laser – A laser directed to the second skin layer to stimulate creation of new skin cells. This approach does not remove the skin surface, causing peeling, as an ablative treatment does.
Neoplasm – A tumor. The term comes from Greek words meaning “new growth”. It can be benign or malignant.
O
Open Rhinoplasty – Nose surgery which uses an external incision in the columella, the fleshy piece between the nostrils, at the end of the septum that divides the nostrils. It also uses internal incisions as done in closed rhinoplasty.
Otoplasty – Ear reshaping surgery.
Outpatient – A patient who does not stay overnight after a surgery and does not receive general anesthesia. Outpatient surgery is done in freestanding clinics or medical centers rather than full-service hospitals.
P
Partial Abdominoplasty – A surgery to remove excess fat and skin from below the navel, rather than from the entire abdomen. Also called a Mini Tummy Tuck.
Periareolar – Referring to the placement of a breast implant incision around the areola.
Perlane® – An injectable filler that restores fullness to the skin, smoothing out deep wrinkles and folds. It is made from hyaluronic acid, a natural body substance that attracts and holds water. The effects of Perlane last six months to a year.
Phenol Peel – The strongest of the chemical skin peels, used to treat deep wrinkles from sun damage and the wrinkles around lips and chin. It removes the skin’s epidermis, thus stimulating the dermis to produce new, tighter cells.
Photo-aging – Aging due to sun exposure, such as wrinkles and age spots.
Plastic Surgery – The surgical specialty that reconstructs areas of the body which are impaired or damaged because of disease, congenital defect, or a disorder. It includes the sub-specialty of cosmetic surgery, which is done for enhancement of physical appearance rather than to restore normality.
Platysmaplasty – Cosmetic surgery to tighten the neck muscles and remove excess skin. The platysma is a wide, flat muscle just beneath the skin on each side of the neck. You can feel it if you pull down the corners of your mouth.
Port wine stain – A birthmark looking the color of port wine, caused by an abnormal concentration of capillaries. It’s a type of hemangioma.
Ptosis – Drooping, as in sagging eyelids or breasts.